The words and language of mechanical seals can be confusing especially since the meanings have evolved. The following terms and definitions are almost, but sometimes not quite, identical to those of API 682 4th Edition. The definitions used in API 682 tend to be specific to the scope and specifications of API 682 whereas the definitions used in SealFAQs are intended to be more general in nature. Where the definitions differ, the words and meaning therein are recommended by the author for use in the next edition of API 682.
A
anti-extrusion ring
backup ring
A ring or disk used to prevent extrusion of an O-ring from its containment.
anti-rotation device
drive mechanism
Device used to prevent rotation of one component relative to an adjacent component in a seal assembly.
Examples: key, pin, slot, dent
Arrangement 1
Single seal
Seal configuration having one seal per cartridge assembly.
Arrangement 2
tandem seal (obsolete)
Seal configuration having two seals per cartridge assembly, with the space between the seals at a pressure less than the seal chamber pressure.
Arrangement 3
double seal (obsolete)
Seal configuration having two seals per cartridge assembly, utilizing an externally supplied barrier fluid at a pressure greater than the seal chamber pressure.
asperities
Minute imperfections on the seal faces.
atmospheric leakage collector
External reservoir arranged to capture liquid seal leakage from an Arrangement 1 seal.
auxiliary equipment
Additional components for seals, usually included in the sealing system such as environmental controls
auxiliary sleeve
A separate sleeve mounted on the outer diameter of the seal shaft sleeve that facilitates assembly of seal components.
axial flow pumping ring
pumping scroll
scroll
Also see internal circulation device. Add drilled vane, slotted, paddle wheel
B
back-to-back configuration
BB
B-B
Dual seal in which both of the seal rings are mounted between the mating rings.
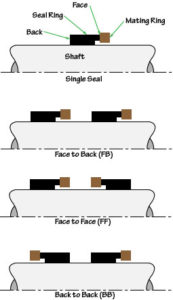
Also see face-to-back and face-to-face
balance diameter
effective diameter
effective balance diameter
The diameter of a mechanical seal at which the resultant force is considered to be acting.
balance ratio
See seal balance ratio
balanced seal
A mechanical seal in which the fluid closing forces have been modified through seal design.
barrier fluid
An externally supplied fluid at a pressure above the pump seal chamber pressure, introduced into an Arrangement 3 seal to completely isolate the process liquid from the environment
barrier/buffer seal chamber
Component or aggregate of components which form the cavity into which the outer seal of a pressurized or unpressurized dual seal is installed and in which a barrier or buffer fluid is circulated.
bellows convolution
An assembly of two formed plates welded at either the inner or outer diameter.
bellows plate
bellows diaphragm
bellows leaflet
A single, thin, metallic disk.
bellows seal
Type of mechanical seal which uses a flexible bellows to provide secondary sealing.
bi-directional seal
double-acting seal
A seal which is designed to operate whether pressure is applied from the outer or inner diameter.
bi-rotational seal
A seal which is designed to operate whether shaft rotation is in either direction.
buffer fluid
Externally supplied fluid, at a pressure lower than the pump seal chamber pressure, used as a lubricant and/or to provide a diluent in an Arrangement 2 seal.
bushing
clearance seal
bush (obsolete)
Cylindrical device with a small annular clearance to the shaft or sleeve which restricts flow between two regions. Also see fixed bushing, floating bushing, segmented bushing.
C
cartridge seal
A completely self-contained unit (including seal faces, flexible elements, seal gland plate and sleeve) which is pre-assembled and preset before installation.
Category 1 seal
A category of API 682 seals which is intended for use in non-API 610 pump seal chambers, meeting the dimensional requirements of ASME B73.1, and ASME B73.2 seal chamber dimensions. Application is limited to seal chamber temperatures from –40 °C (–40 °F) to 260 °C (500 °F) and maximum dynamic sealing pressures pressures up to 2 MPa (20 bar) (300 psi).
Category 2 seal
A category of API 682 seals which is intended for use in seal chambers meeting the seal chamber envelope dimensional requirements of API 610. Application is limited to seal chamber temperatures from –40 °C (–40 °F) to 400 °C (750 °F) and maximum dynamic sealing pressures up to 4 MPa (40 bar) (600 psi).
Category 3 seal
A category of API 682 seals which has the most exact testing and documentation requirements. They meet the seal chamber envelope requirements of API 610 (or equal). Application is limited to seal chamber temperatures from –40 °C (–40 °F) to 400 °C (750 °F) and maximum dynamic sealing pressures up to 4 MPa (40 bar) (600 psi).
cavitation
A condition in which vapor or gas bubbles occur locally in liquids due to local pressure decreases.
coefficient of friction
The ratio of the friction force at the seal faces to the net closing force.
coking
carbonization
The carbonaceous residue formed by reduction of hydrocarbon compounds.
connection
Threaded or flanged joint that mates a port to a pipe or to a piece of tubing.
contacting seal
Seal design in which the mating faces are not designed to intentionally create aerodynamic or hydrodynamic forces to sustain a specific separation gap.
containment device
A seal or bushing which is intended to manage leakage from the inner or outer seal and divert it to a location determined by the user. Includes containment seals.
containment seal
A special version of an outer seal used in Arrangement 2 which normally operates in vapor (whether gas buffer or vaporized process fluid) but will seal the process fluid for a limited time in the event of an inner seal failure.
containment seal chamber
Component or aggregate of components which form the cavity into which the containment seal is installed
containment seal chamber leakage collector
A reservoir, connected by pipework to the containment seal chamber for the purpose of collecting condensed leakage from the inner seal of an Arrangement 2.
crystallizing fluid
Fluid which is in the process of forming solids or which may form solids due to dehydration or chemical reaction
D
distributed flush system
Arrangement of holes, passages, baffles, etc., designed to promote an even distribution of flush fluid around the circumference of the seal faces.
drive collar
External part of the seal cartridge that transmits torque to the seal sleeve and prevents axial movement of the seal sleeve relative to the shaft.
dual mechanical seal
Arrangement 2 or Arrangement 3 seal of any type or category.
durometer
An index used for ranking the relative hardness of elastomers.
dynamic sealing pressure rating
Highest pressure differential that the seal assembly can continuously withstand at the maximum allowable temperature while the shaft is rotating. Thereafter, the seal retains its static sealing pressure rating.
dynamic secondary seal
A secondary seal which is designed to slide or move relative to other components to allow axial movement of the flexible element.
E
elastomer
A natural or synthetic rubber used to make O-rings, bellows and gaskets.
elastomeric bellows seal
A type of mechanical seal that uses an elastomeric bellows for secondary sealing. It is not acceptable to API 682.
engineered seal
Mechanical seal for applications with service conditions outside the operation scope of the Type A, B and C seals of API 682.
externally pressurized seal
OD pressurized seal
A seal activated by pressure from the outside diameter of the seal faces.
external circulating device
Device located outside of the seal/buffer/barrier chamber to circulate seal chamber fluid through a cooler or barrier/buffer fluid reservoir.
F
face-to-back configuration
FB
F-B
Dual seal in which one mating ring is mounted between the two seal rings and one seal ring is mounted between the two mating rings.

Also see back-to-back and face-to-face
face-to-face configuration
FF
F-F
opposed seals
Dual seal in which both of the mating rings are mounted between the seal rings.

Also see back-to-back and face-to-back
fixed bushing
clearance seal
fixed bush (obsolete)
Cylindrical device with a close clearance to the shaft or sleeve which restricts flow between two regions and which does not have a clearance on the outer diameter relative to the housing in which it is mounted
fixed throttle bushing
fixed throttle bush (obsolete)
One piece cylindrical device that is fitted to the stationary part of the containment seal chamber and has a radial clearance to a rotating component. It is used to help isolate one region from another and assist in channeling liquid leakage to an exit port. The design is intended to maintain a fixed radial clearance over the operating life of the seal.
flashing
Rapid change of fluid state from liquid to gas
flashing hydrocarbon
flashing fluid
Liquid hydrocarbon or other fluid with an absolute vapor pressure greater than 0,1 MPa [1 bar] [14,7 psi] at the pumping temperature, or a fluid that will readily boil at ambient conditions
flexible element
Combination of elements which accommodate axial movement of between rotating and stationary parts
flexible graphite
Exfoliated and recompressed graphite material used for static secondary seals and gaskets in mechanical seals.
floating bushing
floating bush (obsolete)
Cylindrical device with a close clearance to the shaft or sleeve which restricts flow between two regions and which has a clearance on the outer diameter relative to the housing in which it is mounted to allow radial motion (“floating”) of the bushing should it come in contact with the rotating shaft or sleeve
fluoroelastomer
FKM
A saturated polymer in which hydrogen atoms have been replaced with fluorine. It is characterized by excellent hydrocarbon and general chemical resistance.
flush
Noun: fluid which is introduced into the seal chamber on the process fluid side in close proximity to the seal faces and typically used for cooling and lubricating the seal faces and/or to keep them clean
Verb: the act of providing a flush fluid to the seal.
G
gland plate
gland end plate
end plate
flange
gland (incomplete)
Pressure retaining component(s) similar to a flange which connects the stationary assembly of a mechanical seal to the seal chamber
Note: a gland plate may consist of more than one pressure containing component for example the two gland plates often used in a dual seal
H
hard face
A seal face of high hardness, typically tungsten carbide or silicon carbide.
hook sleeve
sleeve with a step (“hook”) near the process fluid end of the shaft that is placed over the shaft to protect the shaft from wear and corrosion.
hydrodynamic seal
A seal with special geometry on one of the faces which is designed to use relative motion to produce non-contacting operation.
hydrostatic test
hydrotest
A pressure test to assure that a pressure vessel does not leak.
I
informative
Supplemental information for which compliance is not required. Also see “normative”.
inner seal
inboard seal (incomplete)
The seal closest to the pump impeller or process fluid in Arrangement 2 and Arrangement 3.
inside mounted seal
internally mounted seal
Seal configuration in which the seal is positioned within the boundaries of the seal chamber or containment seal chamber or gland plate,
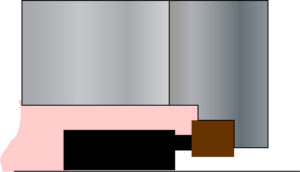
Also see externally mounted seal
internally pressurized seal
ID pressurized seal
A seal activated by pressure from the inside diameter of the seal faces.
internal circulating device
pumping ring
pumping scroll
Device located in the seal buffer/barrier chamber to circulate fluid through a cooler or barrier/buffer fluid reservoir
L
leakage concentration
emission rate (misleading)
Measure of the concentration of a volatile organic compound or other regulated emission in the environment immediately surrounding the seal
leakage rate
emission rate (misleading)
Volume or mass of fluid passing through a seal in a given length of time.
light hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon liquid that will readily boil at ambient conditions.
M
mating ring
seat
Disk or toroidal-shaped member, mounted either on a sleeve or in a housing such that it does not move axially relative to the sleeve or the housing on or which it is mounted, and, which provides the mating seal face for the seal ring face. The mating seal face is perpendicular to the axis of the shaft.
maximum allowable temperature
Maximum continuous temperature for which the manufacturer has designed the equipment (or any part to which the term is referred) when handling the specified fluid at the specified maximum operating pressure
maximum allowable working pressure
MAWP
Maximum continuous pressure for which the manufacturer has designed the equipment (or any part to which the term is referred) when handling the specified fluid at the specified maximum operating temperature. Also, see static sealing-pressure rating and dynamic sealing-pressure rating.
maximum dynamic sealing pressure
MDSP
Highest pressure expected at the seal (or seals) during any specified operating condition and during start-up and shutdown.
Note 1: This is a process condition and is specified by the purchaser.
Note 2: In determining this pressure, consideration is given to the maximum suction pressure, the flush pressure, and the effect of clearance changes within the pump.
maximum operating temperature
maximum temperature to which the seal (or seals) can be subjected
Note: This is a process condition and is specified by the purchaser.
maximum static sealing pressure
MSSP
Highest pressure, excluding pressures encountered during hydrostatic testing, to which the seal (or seals) can be subjected while the pump is shut down
N
non-contacting seal
self-acting seal
Seal design in which the faces are designed to intentionally create aerodynamic or hydrodynamic separating forces to sustain a specific separation gap between the seal ring and the mating ring
non-flashing hydrocarbon
non-flashing fluid
Liquid hydrocarbon or other fluid whose vapor pressure at any specified operating temperature is less than an absolute pressure of 0,1 MPa [1 bar] [14,7 psi], or a fluid that will not readily boil at ambient conditions
non-hydrocarbon service
Service in which the fluid, such as sour water, boiler feed water, sodium hydroxide, acids and amines, contains no hydrocarbons or the fluid has relatively small quantities of entrained hydrocarbons
normative
A requirement conveying criteria to be fulfilled if compliance is to be claimed. Also see “informative”.
O
observed test
Product test which is observed at the discretion of the purchaser, who has been given notice of the test by the manufacturer, but does not constitute a manufacturing hold point
orifice nipple
Pipe nipple made of solid bar stock with an orifice hole drilled through it to restrict leakage in the event of an auxiliary system pipe or component failure
O-ring
Elastomeric sealing ring with an O-shaped (circular) cross-section, which may be used as either a static or dynamic secondary seal.
outer seal
The seal located farthest from the pump impeller or process fluid in Arrangement 2 and Arrangement 3.
outside mounted seal
externally mounted seal
Seal configuration in which the seal is positioned outside the boundaries of the seal chamber or containment seal chamber or gland plate
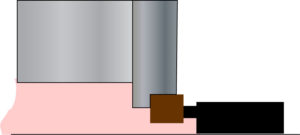
Also see inside mounted seal
P
perfluoroelastomer
FFKM
A fully fluorinated fluorocarbon elastomer commonly used as a secondary seal in high temperature and/or corrosive service
piping plan
Configuration of accessories, instruments, controls and/or fluids designed to manage or control the environment around the seal
polymerizing fluid
Fluid which is in the process of changing, or is capable of changing, from one chemical composition to another with longer-chain components and different properties, usually becoming significantly more viscous and/or tacky
port
Fluid passageway, typically located in the gland plate
pressure casing
Composite of all the stationary pressure-containing parts of the seal, including seal chamber barrier or buffer fluid chamber, containment seal chamber and seal gland plate, and excluding seal ring, mating ring, bellows, sleeves, miscellaneous internal seal parts and atmospheric side gland connections which cannot be isolated from atmospheric pressure.
pressure reversal
A condition where the pressure differential changes from the outer diameter to the inner diameter or vice versa.
product temperature margin
Difference between the vaporization temperature of the fluid at the seal chamber pressure and the actual temperature of the fluid
pump manufacturer
pump OEM
Agency that designs, manufactures, tests and provides service support for the pump
pumped fluid
process fluid
pumpage
Fluid/liquid that is the process stream designated in the data sheet for the pump service
purchaser
Agency that issues the order and specifications to the vendor
pusher seal
A seal which incorporates a dynamic secondary seal to allow axial movement of the flexible element. The axial movement is driven (pushed) by mechanical and/or hydraulic force
PV factor
PV value
PV
The product of average seal face pressure and relative sliding velocity.
Q
quench
Noun: neutral fluid, usually water, steam or nitrogen introduced on the atmospheric side of the seal to retard formation of solids that may interfere with seal movement, or for other purposes such as prevention of coking, crystallization or icing
Verb: to supply a quench fluid
R
retainer
The portion of the seal head that contains the seal ring.
reservoir
seal pot
A container or tank used to hold a buffer or barrier fluid for a dual seal system.
S
seal
end face mechanical seal
face seal
mechanical seal
A device that prevents the leakage of fluids between a shaft and housing in relative motion. Sealing is accomplished by a stationary seal face bearing against the face of a rotating seal ring. The sealing faces are mounted perpendicular to the shaft axis.
seal assembly
A collection of seal components in built up form
seal balance ratio
balance ratio
Ratio of seal face area exposed to closing force by hydraulic pressure in the seal chamber, to the total seal face area. Sometimes expressed as a percentage.
seal chamber
seal cavity
stuffing box (obsolete)
Component, either integral with or separate from the pump case (housing), that forms the region between the shaft and casing into which the seal is installed
seal head
An assembly of parts comprising the complete functional unit of the flexible unit of the seal.
seal face
seal faces
mating face
The lapped surface of a mating ring or seal ring which comes in contact or close proximity to the other ring and provides the relative rotary motion sealing surface(s).
seal face pressure
face pressure
The net force on the seal faces divided by the face area.
seal manufacturer
seal OEM
Agency that designs, manufactures, tests, and provides service support for seals and associated support sealing systems
seal ring
primary ring
washer (obsolete)
Disk or torrodial shaped member, mounted either on a sleeve or in a housing such that it is able to move axially relative to the sleeve or the housing on or in which it mounted, and which provides the mating seal face for the mating ring face. The seal ring face is perpendicular to the axis of the shaft.
seal sleeve
Hollow cylindrical component which fits on the outer diameter of the shaft with a close tolerance fit, incorporates a static secondary seal with the shaft and extends beyond the seal gland plate. It is used in the assembly of the seal components and ensures they rotate with the shaft
secondary seal
A device (such as an O-ring, flexible graphite ring, flexible graphite filled spiral wound gasket, or bellows) that prevents leakage of the sealed fluid, barrier fluid, buffer fluid or quench medium through paths other than the inner or outer seal faces, the containment device or designated drain.
segmented floating bushing
A throat or throttle bushing which is composed of circumferential segments retained by a tensioning device.
spring pressure
The force exerted by the seal spring divided by the seal face area.
service condition
Maximum or minimum temperature or pressure under static or dynamic conditions
static sealing-pressure rating
Highest pressure that the seal can continuously withstand at the maximum allowable temperature while the shaft is not rotating. Thereafter, the seal maintains its dynamic sealing pressure rating.
static secondary seal
A secondary seal between two surfaces which have no relative motion.
strainer
A relatively low pressure drop device designed to remove solid particles from the flush or other fluid.
U
U-cup
Elastomeric sealing ring with an U-shaped (circular) cross-section, which may be used as either a static or dynamic secondary seal.
Note: Not recommended by API 682.
unbalanced seal
A mechanical seal for which the seal balance ratio is less than 1.
uni-directional seal
single-acting seal
A seal which is designed to operate only when pressure is applied from either the outer or inner diameter but not both.
uni-rotational seal
A seal which is designed to operate with shaft rotation from only one direction.
V
V-ring
Elastomeric sealing ring with an V-shaped (circular) cross-section, which may be used as either a static or dynamic secondary seal.
Note: Not recommended by API 682.
vendor
Manufacturer of the equipment, or his agent, normally responsible for service support
volatile hazardous air pollutant
VHAP
Any compound as defined by Title 1, Part A, Section 112 of the U.S. National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAPs) (Clean Air Act Amendment)
W
Wedge
Wedge ring
Elastomeric sealing ring with a wedge shaped (circular) cross-section, which may be used as either a static or dynamic secondary seal. Often made of PTFE.
witnessed inspection
witnessed test
Inspection or test for which the purchaser is notified of the timing and a hold is placed on production until the purchaser or his representative is in attendance
T
throat bushing
neck bush (obsolete)
Device that forms a restrictive close clearance around the sleeve (or shaft) between the seal chamber and the impeller
throttle bushing
A containment device that forms a restrictively close clearance around the sleeve at the atmospheric end of a gland plate
total indicator reading
total indicated runout
TIR
Difference between the maximum and minimum readings of a dial indicator or similar device when monitoring a face or cylindrical surface during one complete revolution of the monitored surface
Type A seal
A balanced, internally-mounted, cartridge design, pusher seal with multiple springs. Secondary sealing elements are elastomeric O-rings.
Type B seal
A balanced, internally-mounted, cartridge design, metal bellows seal. Secondary sealing elements are elastomeric O-rings.
Type C seal
A balanced, internally-mounted, cartridge design (metal bellows) seal. Secondary sealing elements are flexible graphite.
